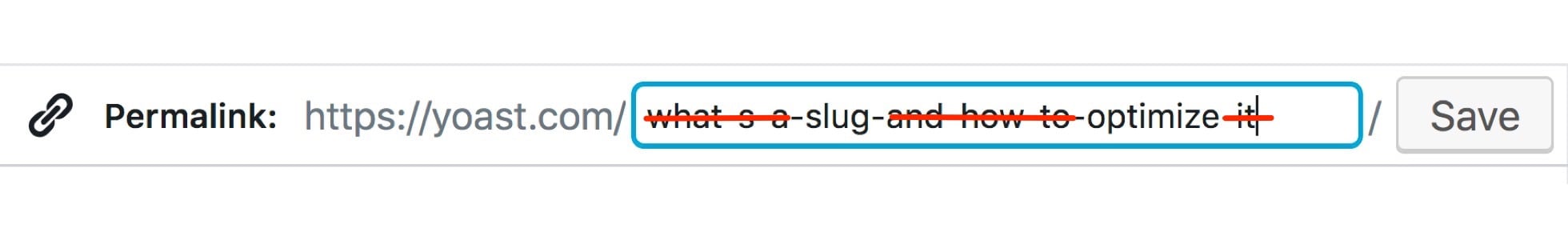
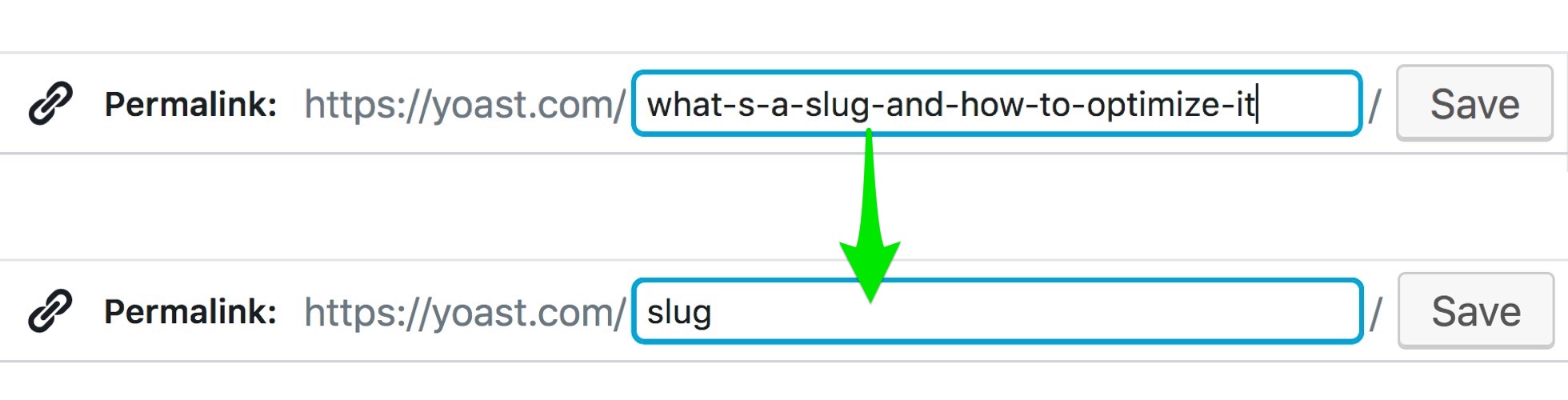
The permalink is the full URL you see – and use – for any given post, page or other pieces of content on your site. It’s a permanent link, hence the name permalink. A permalink could include your domain name (www.yoast.com) plus what’s called a slug, the piece of the URL that comes after the domain name. This might include a date or a category or anything you please. A simple permalink makes a URL easy to understand and share. In this SEO basics article, we’ll take a closer look at the permalink.
Permalinks should be SEO-friendly
Permalinks are an important part of your site as both search engines and visitors use these URLs to index and visit your site. The type of permalink you pick influences the way these two parties see and value your site. A URL with a load of incomprehensible gibberish at the end is a lot less shareable and enticing than a short and simple SEO-friendly URL. An example permalink could be:
https://www.yoast.com/category/post-nameIt could also be something like:
https://www.yoast.com/10/10/2017/post-nameor
https://yoast.com/post-nameBy default, WordPress uses a permalink structure that’s not SEO-friendly. These look something like this:
https://yoast.com/?p=101The number you see is the ID WordPress had in mind for this particular article. It’s article number 101 in the database of your site. While Google still understands the content on that page, a URL like this does nothing for your SEO. It does not describe what kind of content the page offers and it’s not something that users are inclined to share. And did we mention that it’s not very professional looking? If your URL contains relevant words, this provides users and search engines with more information about the page than any ID or parameter would.
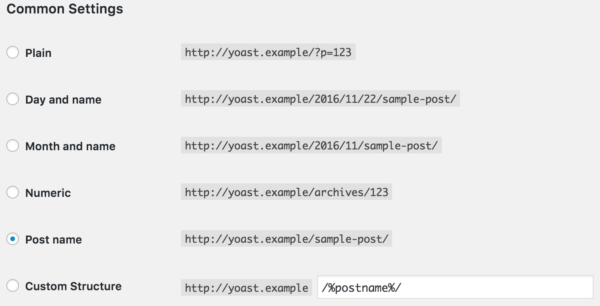
Considerations for your permalinks
Make sure you pick a permalink structure that fits your goals. If you have a news site, it might make sense to add the publication date of the article to the URL. If, however, you are planning to write killer cornerstone content that has to stand the test of time, it’s not recommended to use a date in the URL as this could make the content look ‘old’.
We recommend using a simple and clear permalink structure. For most sites, it makes sense to append the post name to the domain name. So in WordPress that would be the /postname/ option. In some cases, a category will help create a hierarchy in the URLs. Keep in mind that this could also result in too long URLs.
Yoast SEO and permalinks
Yoast SEO is a must-have tool that makes SEO available to everyone. It’s an easy to use tool that helps you make a perfect website. For instance, if you install WordPress and don’t change the default permalink settings, Yoast SEO will urge you to change it. Yoast SEO has several other options that can help you clean up those permalinks, like stripping the category base (usually category).
If you’re changing a permalink or deleting a page, we prevent users from landing on a 404 error page. Yoast SEO Premium has a brilliant redirect manager that helps you do that. It will create a 301 redirect automatically if you change the permalink of a page. In addition to that, it asks if you’d like to create a 301 redirect if you delete a page. Just enter the URL you want your visitors to go to and you’re done!
Finally, a word of warning
Pick your permalink structure wisely. Don’t change your permalink structure for the sake of it. Incorrectly redirecting your old URLs to the new URLs might lead to problems and could get you dropped from the rankings. Please think about your permalink structure before launching your site. Should you need to change your permalinks you can find more information on how to change your permalink structure or visit Google’s page on moving your site.
Read more: Why every website needs Yoast SEO »
The post What is a permalink? appeared first on Yoast.